The Advanced High-Temperature Reactor (AHTR) concept leverages a particle-based fuel format consisting of discrete spherical graphite pebbles arrayed in a packed bed architecture. Thermal regulation achieved via flow of gas (e.g., helium) or liquid (e.g., molten salt) coolants through the void spaces between pebbles in the bed (characteristic pebble diameters: ~ 6 cm, gas cooled; ~ 3 cm, liquid cooled).
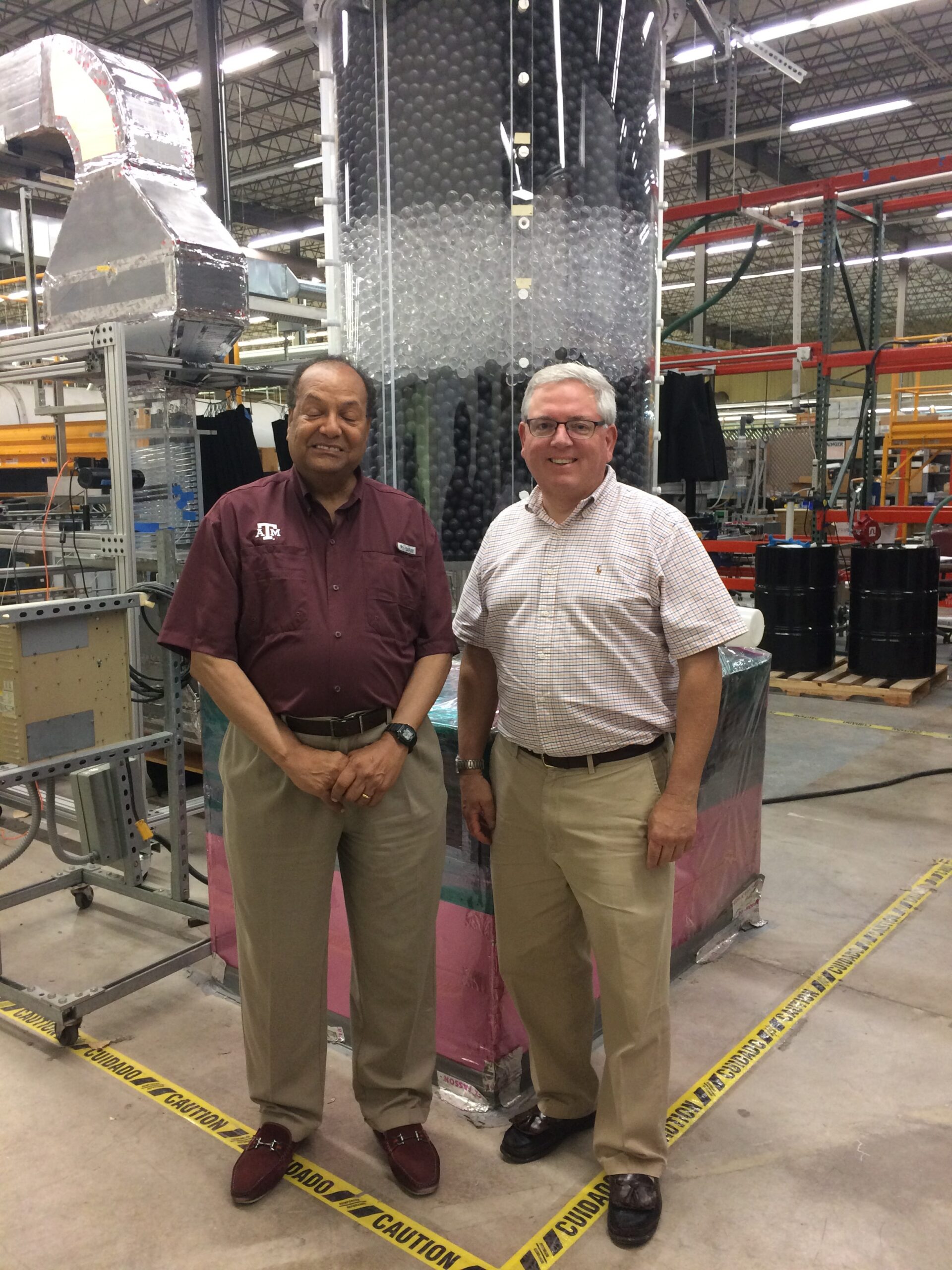
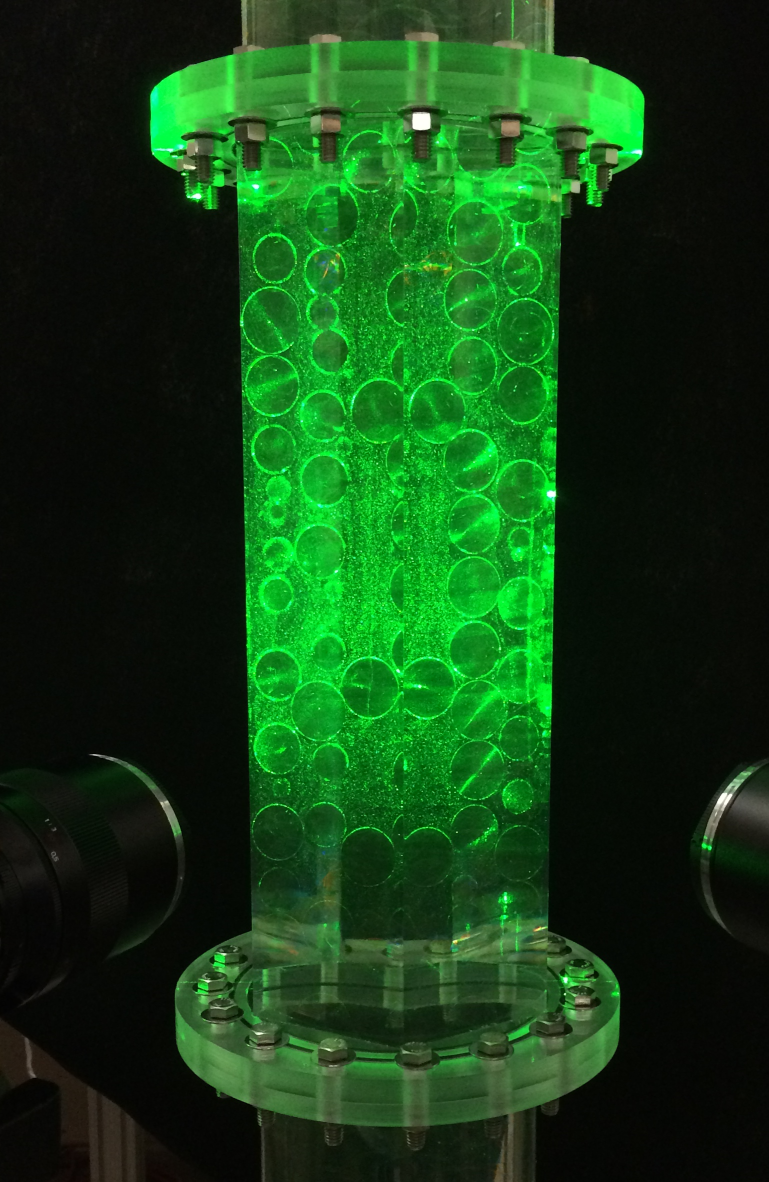 Texas A&M is conducting pressure drop and velocity measurements in the versatile experimental facility of randomly packed spheres at various Reynolds numbers. High-fidelity velocity measurements using Time-resolved Stereoscopic Particle Image Velocimetry (TR-SPIV) at the pore scales and near the wall boundary are performed in the matching-refractive-index (MRI) facility.
Texas A&M is conducting pressure drop and velocity measurements in the versatile experimental facility of randomly packed spheres at various Reynolds numbers. High-fidelity velocity measurements using Time-resolved Stereoscopic Particle Image Velocimetry (TR-SPIV) at the pore scales and near the wall boundary are performed in the matching-refractive-index (MRI) facility.